DIABETIC FOOT
WHAT IS DIABETIC FOOT?
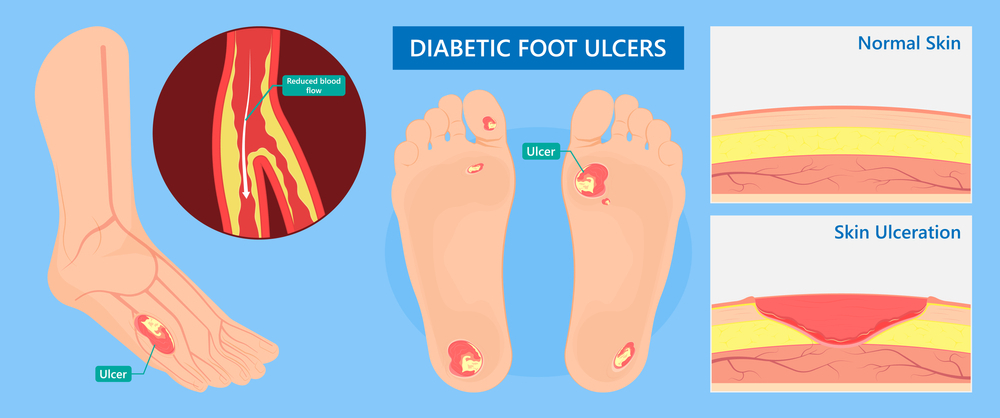
Diabetic foot refers to a group of foot problems that can occur in people with diabetes. Diabetes can lead to complications that affect the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, making them more susceptible to injury and slower to heal. The condition can range from mild to severe and, if left untreated, may lead to serious complications, including infections and amputations.
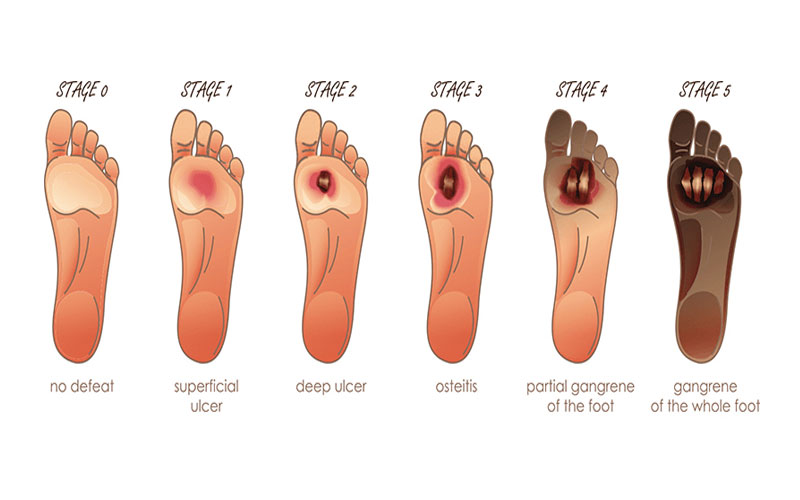
LIST OUT THE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETIC FOOT?
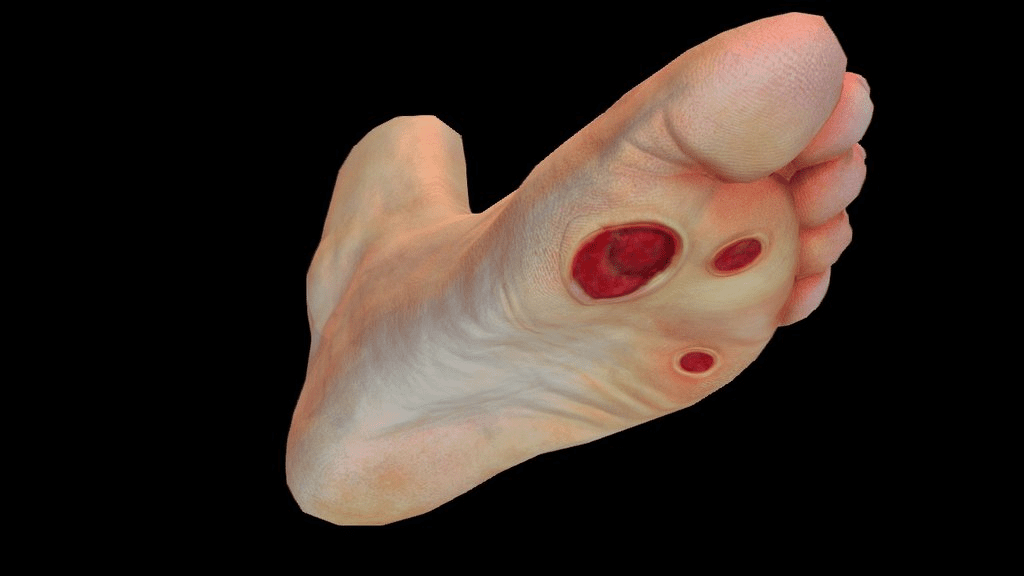
1.Foot Ulcers:
2.Infections:
Due to compromised immune function in diabetes, even minor injuries or ulcers can become infected. Infections in the feet can spread to the surrounding tissues and, if not treated promptly, may lead to more serious complications.
3.Cellulitis:
This is a bacterial skin infection that can occur in the lower limbs, often starting from a wound or ulcer. It can cause redness, swelling, and pain.
4.Osteomyelitis:
If an infection reaches the bone, it can lead to osteomyelitis, which is a serious and often chronic bone infection. This condition may require prolonged antibiotic treatment and, in severe cases, surgery.
5.Gangrene:
Reduced blood flow and untreated infections can result in tissue death (gangrene). Gangrene is a serious condition that may necessitate amputation to prevent the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
6.Charcot Foot:
This condition involves the weakening of the bones in the foot, leading to fractures and joint deformities. It is often associated with neuropathy, and individuals may not be aware of the damage occurring to their feet.
7.Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
Diabetes can contribute to the development of PAD, which is characterized by reduced blood flow to the extremities. Poor circulation can impede the healing of wounds and increase the risk of infections.
8.Foot Deformities:
Chronic complications, such as Charcot foot and repetitive trauma, can result in deformities that affect the structure and function of the foot.
9.Amputation:
In severe cases, when complications like infections or gangrene become uncontrollable, amputation may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection and preserve overall health.
List out the prevention of diabetic foot?
1.Daily Foot Inspection:
- Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or any signs of injury.
- Use a mirror or ask someone for assistance if it’s challenging to inspect the soles of your feet.
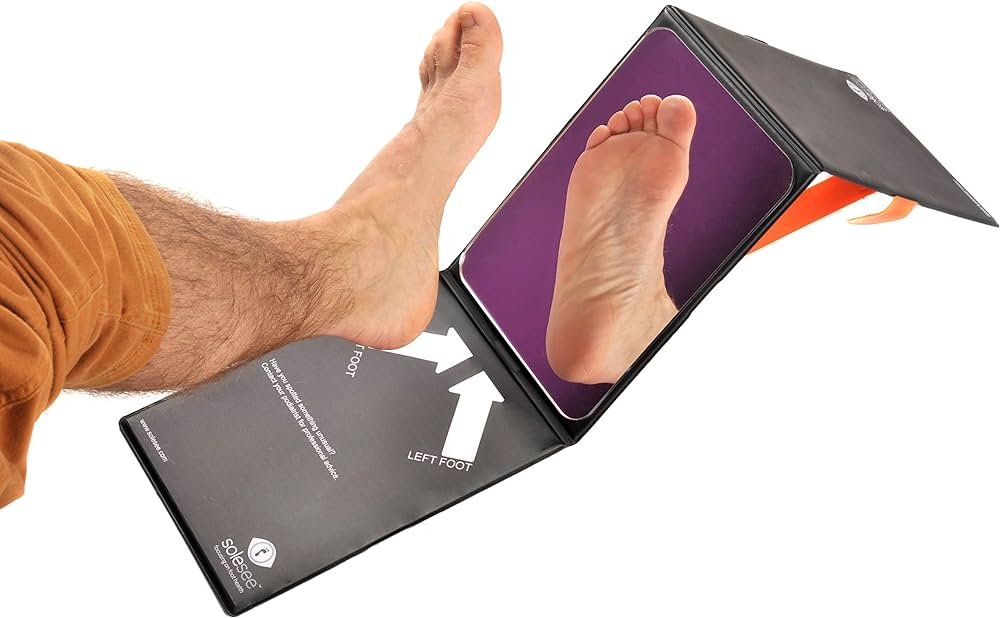
2.Proper Foot Hygiene:
- Wash your feet daily with mild soap and lukewarm water.
- Gently dry your feet, paying attention to the spaces between the toes.
3.Moisturize Carefully:
- Apply a thin layer of moisturizer to prevent dry skin, but avoid applying it between the toes to prevent moisture buildup.
4.Trim Nails Carefully:
- Trim your toenails straight across and file the edges to avoid ingrown toenails.
- If you have difficulty trimming your nails, consider seeking professional help from a podiatrist.
5.Wear Proper Footwear:
- Choose shoes that fit well and provide proper support.
- Avoid tight shoes and opt for those made of breathable materials (MCR SLIPERS).
- Check your shoes regularly for any foreign objects, rough spots, or seams that might cause irritation.
6.Diabetic Socks:
- Wear clean, dry socks that don’t have seams or tight elastic bands.
- Consider diabetic socks designed to reduce pressure and moisture.
7.Regular Exercise:
- Engage in regular physical activity to promote circulation and overall health.
- Consult with your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program.
8.Blood Sugar Control:
- Maintain good blood sugar control through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication as prescribed by your healthcare team.
9.Regular Medical Checkups:
- Schedule regular checkups with your healthcare provider, including foot examinations.
- Report any foot problems promptly.
10.Avoid Smoking:
- Smoking can impair circulation, so quitting can benefit your overall vascular health, including the blood flow to your feet.
11.Manage Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD):
- Work with your healthcare provider to manage conditions that may contribute to poor circulation, such as PAD.
12.Educate Yourself:
- Learn about proper foot care and diabetes management through educational programs or materials provided by healthcare professionals.
13.Prompt Treatment of Foot Issues:
- Seek immediate medical attention for any signs of infection, ulcers, or other foot problems.
- Do not attempt to self-treat serious foot issues.
14.Foot Elevation:
- Elevate your feet when sitting to reduce swelling and improve circulation.
LIST OUT THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC FOOTS ?
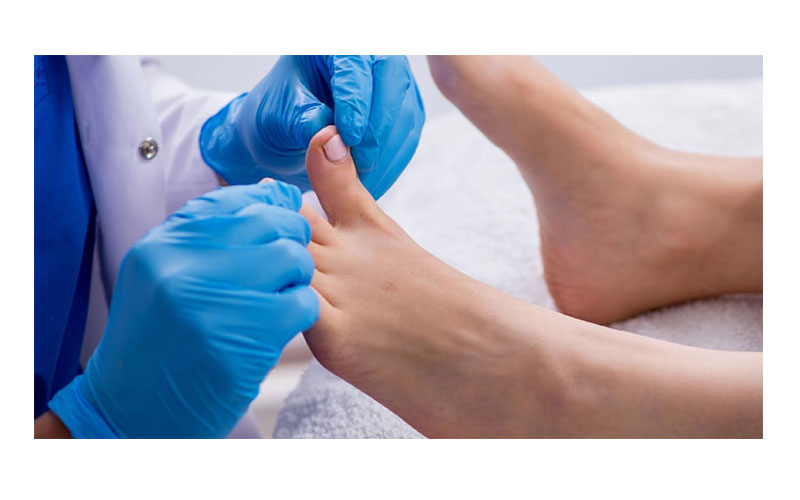
1.Wound Care:
- Cleaning and Dressing: Proper cleaning and dressing of wounds to prevent infection. This may involve removing dead tissue (debridement) and applying topical medications.
- Offloading: Reducing pressure on the affected area to promote healing. This may involve the use of special footwear, casts, or orthotic devices.
2.Infection Management:
- Antibiotics: Prescribing antibiotics to treat bacterial infections. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type and severity of the infection.
- Surgical Intervention: In more severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue.
3.Blood Sugar Control:
- Medication Management: Ensuring that diabetes medications, including insulin, are taken as prescribed to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise routine to help control blood sugar levels.
4.Vascular Interventions:
- Revascularization: In cases of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be considered to improve blood flow to the affected area.
5.Foot Elevation:
- Elevating the Feet: Elevating the feet when sitting to reduce swelling and improve circulation.
6.Offloading Devices:
- Custom Footwear: Prescribing custom-made shoes or orthotic inserts to redistribute pressure on the feet and prevent further damage.
7.Education:
- Patient Education: Providing education on proper foot care, including daily foot inspections, hygiene practices, and the importance of seeking medical attention for any issues.
8.Pain Management:
- Pain Medications: Prescribing pain medications to manage discomfort associated with diabetic foot complications.
9.Follow-up Care:
- RegularMonitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor the progress of treatment, adjust medications, and address any emerging issues.
10.Multidisciplinary Team Approach:
- Collaboration: Involving a multidisciplinary team, including podiatrists, endocrinologists, vascular surgeons, and physician, to ensure comprehensive care.
WHY I CHOOSE PLASTIC SURGEON FOR DIABETIC FOOT?
1.Wound Debridement:
- Plastic surgeons may perform precise surgical debridement, which involves the removal of dead or infected tissue from wounds. This is crucial for promoting healing and preventing the spread of infection.
2.Soft Tissue Reconstruction:
- In cases where extensive tissue loss or damage has occurred, plastic surgeons may perform soft tissue reconstruction. This may involve the use of flaps or grafts to repair and restore the affected area.
3.Skin Grafts:
- Plastic surgeons may use skin grafts to cover large wounds or areas where tissue has been lost. Skin grafts involve taking skin from one part of the body (donor site) and transplanting it to the affected area.
4.Reconstructive Surgery for Deformities:
- In cases of severe deformities, such as those resulting from Charcot foot, plastic surgeons may perform reconstructive surgery to correct and stabilize the bone and joint structures.
5.Microsurgery:
- Microsurgical techniques may be employed by plastic surgeons to reestablish blood flow in cases of severe vascular compromise. This could be particularly relevant in diabetic foot complications associated with peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
6.Pressure Offloading Devices:
- Plastic surgeons may collaborate with other specialists in designing and implementing pressure offloading devices, such as custom orthotics or braces, to alleviate pressure on specific areas of the foot and promote healing.
7.Scar Revision:
- After wounds have healed, plastic surgeons may perform scar revision procedures to improve the appearance and functionality of scars resulting from previous surgeries or injuries.
8.Collaboration with Other Specialists:
- Plastic surgeons is crutial role often work as part of a multidisciplinary team that may include vascular surgeons, orthopedic surgeons, podiatrists, and other healthcare professionals. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive care for individuals with diabetic foot complications.
